Structural Properties of Protein–Detergent Complexes from SAXS and MD Simulations
Abstract
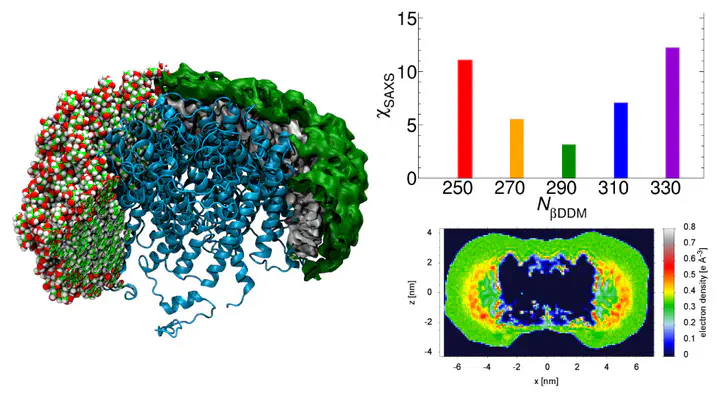
In experimental studies of solubilized membrane proteins, the detergent corona influences the protein behavior and the resulting measurement. Thus, combinations of experimental techniques with atomistic modeling have been used to resolve corona structural parameters and distributions. Here, we used small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) data and molecular dynamics simulations to study a model protein–detergent complex (PDC) consisting of aquaporin-0 and dodecyl-β-maltoside molecules (βDDM). The corona morphology of single snapshots was found to be rough, but it is smooth and compacted in 100-ns-scale ensemble averages. Individual snapshots therefore were unable to accurately represent the ensemble information as captured by experimental SAXS. Mimicking of annular lipids by detergent was also observed. SAXS prediction using different published methods was used to identify optimal βDDM numbers. Explicit-solvent methods predicted best agreement using 290-βDDM PDCs, but implicit-solvent methods gave unclear predictions due to overcompensation by free solvation-layer density parameters. Thus, ensemble-based approaches and physically motivated constraints will help to extract structural information from SAXS data.